摘要:本文解释了同步发电机的工作原理,包括定义和实际应用。同步发电机是一种能够根据实地数据评估执行的设备,它通过转换机械能为电能来工作。文章深入阐述了同步发电机的操作过程,帮助读者理解其在现代电力系统中的重要性和应用。
In the realm of electrical engineering, the synchronous generator is a pivotal component that plays a crucial role in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Its operation is not only a technical marvel but also a testament to the advancements in power generation technology. Let us delve into the intricacies of how a synchronous generator works and its definition with a practical approach.
Definition of Synchronous Generator:
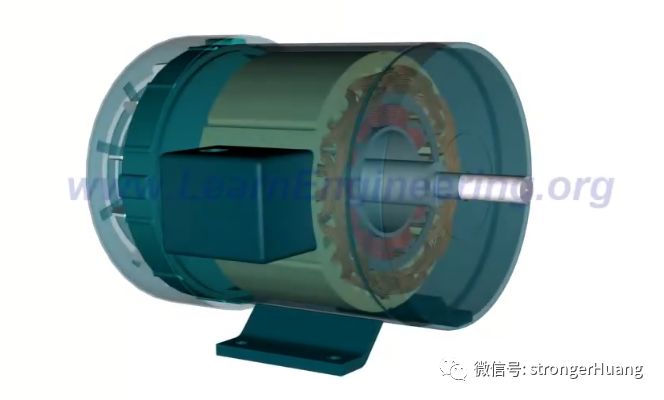
A synchronous generator is an electrical machine that converts mechanical energy from a prime mover into electrical energy, typically in the form of alternating current (AC). It operates at a constant speed and produces a sinusoidal waveform, hence the term "synchronous." The generator's rotor is connected to a source of mechanical energy, such as a turbine or motor, and rotates at a specific speed to generate electricity.
How Synchronous Generator Works:
1、Mechanical Energy Conversion: The synchronous generator's operation begins with the conversion of mechanical energy from a prime mover, such as a steam turbine or gas turbine, into rotational motion. The rotor of the generator is connected to this prime mover and rotates at a specific speed determined by the frequency of the generated electricity.
2、Magnetic Field Generation: As the rotor rotates, it carries conductors through a magnetic field, which is created by permanent magnets or electromagnetic fields generated by current-carrying windings on the generator's stator. This interaction between the rotating conductors and the magnetic field induces an electrical current in the rotor's windings.
3、AC Generation: The induced current in the rotor's windings is in the form of AC (alternating current). The frequency of this AC is directly related to the speed of rotation and is typically measured in cycles per second or Hertz (Hz). In most cases, the synchronous generator operates at a constant speed to maintain a constant frequency of the generated AC power.
4、Power Output: The AC power generated by the synchronous generator is then transmitted to the power grid through transformers and other transmission equipment. The generator's output voltage and frequency are regulated to match the grid's requirements, ensuring a stable supply of electricity to consumers.
Real-World Application and Explanation:
The synchronous generator's operation is not only theoretical but also highly practical in real-world applications. Its widespread use in power stations and other power generation facilities makes it a crucial component in maintaining a reliable and efficient power supply.
1、Power Stations: Synchronous generators are commonly used in power stations to convert the mechanical energy from turbines into electrical energy. The generators are connected to the turbines through shafts and rotate at high speeds to generate electricity. This electricity is then transmitted to the power grid for distribution to consumers.
2、Voltage Regulation: One of the key functions of a synchronous generator is voltage regulation. As the load on the generator changes, the generator's field current is adjusted to maintain a constant voltage output. This ensures that the power supply remains stable even during variations in demand.
3、Frequency Control: Similarly, the synchronous generator also plays a crucial role in maintaining frequency stability. The speed of the generator's rotor is adjusted to maintain a constant frequency of the generated AC power, typically at 50 Hz or 60 Hz, depending on the country's power grid standards.
4、Parallel Operation: In large power stations, multiple synchronous generators can operate in parallel to provide additional power output. This allows for greater flexibility in adjusting power output and maintaining stability during variations in demand or supply.
In conclusion, the synchronous generator is a pivotal component in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Its operation involves complex interactions between mechanical energy, magnetic fields, and electrical currents to generate AC power. The real-world applications of synchronous generators in power stations and other power generation facilities make them crucial for maintaining a reliable and efficient power supply. Understanding the working principles of synchronous generators is essential for ensuring their optimal performance and reliability in power generation systems.



 黔ICP备2023012121号-1
黔ICP备2023012121号-1 黔ICP备2023012121号-1
黔ICP备2023012121号-1
还没有评论,来说两句吧...